Since people are wanting to talk about the latest events on the Antarctic Peninsula, this is a post for that discussion.
The imagery from ESA (animation here) tells the recent story quite clearly – the last sliver of ice between the main Wilkins ice shelf and Charcot Island is currently collapsing in a very interesting way (from a materials science point of view). For some of the history of the collapse, see our previous post. This is the tenth major ice shelf to collapse in recent times.
Maybe we can get some updates and discussion of potential implications from the people working on this in the comments….?
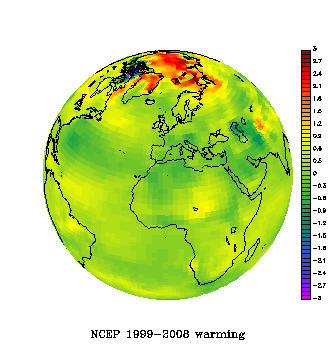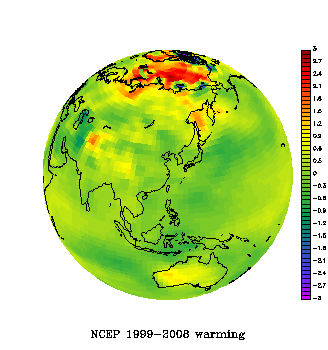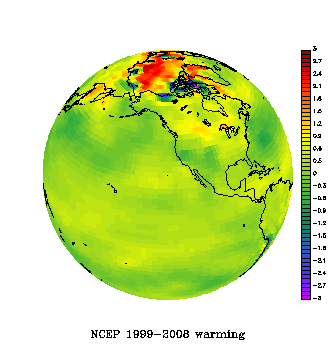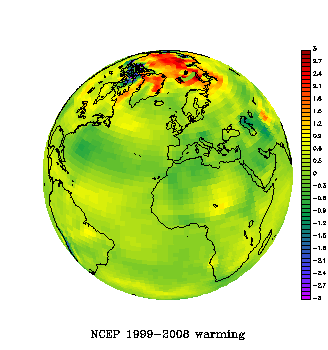
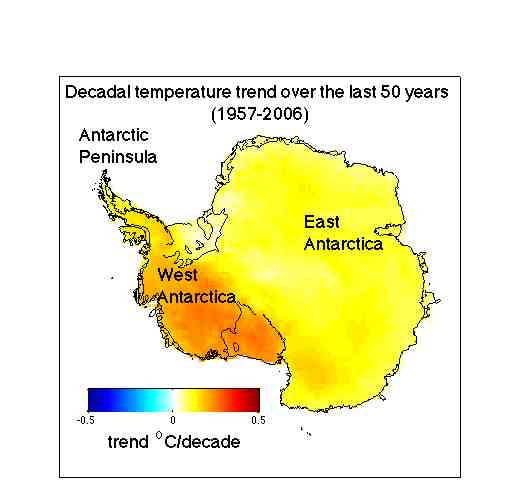 The paper shows that Antarctica has been warming for the last 50 years, and that it has been warming especially in West Antarctica (see the figure). The results are based on a statistical blending of satellite data and temperature data from weather stations. The results don’t depend on the statistics alone. They are backed up by independent data from automatic weather stations, as shown in our paper as well as in updated work by Bromwich, Monaghan and others (see their AGU abstract,
The paper shows that Antarctica has been warming for the last 50 years, and that it has been warming especially in West Antarctica (see the figure). The results are based on a statistical blending of satellite data and temperature data from weather stations. The results don’t depend on the statistics alone. They are backed up by independent data from automatic weather stations, as shown in our paper as well as in updated work by Bromwich, Monaghan and others (see their AGU abstract,