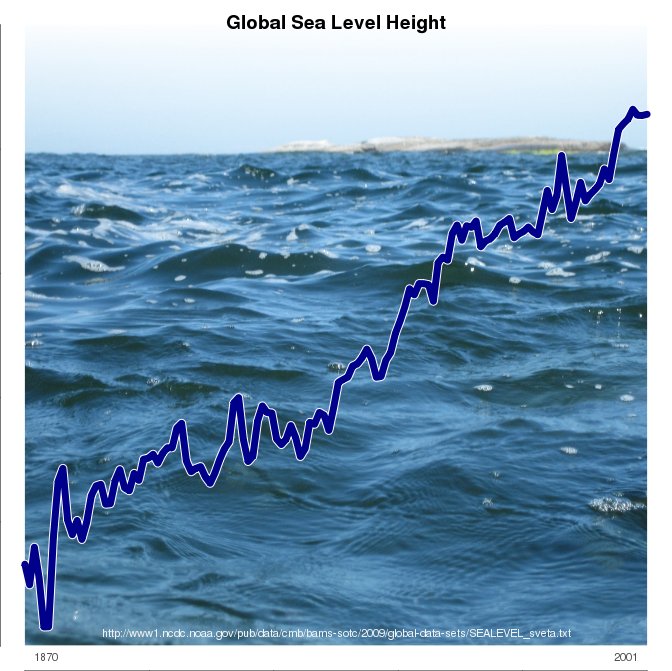
A while ago, I received a request to publish a paper on a post that I had written here on RealClimate, exposing the flaws in the analysis of Humlum et al., (2011).
Instead of writing a comment to one paper, however, I thought it might be useful to collect a sample of papers that I found unconvincing (usual suspects), and that have had a fairly high public profile.
[Read more…] about A new experiment with science publication
References
- O. Humlum, J. Solheim, and K. Stordahl, "Identifying natural contributions to late Holocene climate change", Global and Planetary Change, vol. 79, pp. 145-156, 2011. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2011.09.005