Eric Steig & Ray Pierrehumbert
 One of my (Eric’s) favorite old books is The Starship and the Canoe by Kenneth Brower It’s a 1970s book about a father (Freeman Dyson, theoretical physicist living in Princeton) and son (George Dyson, hippy kayaker living 90 ft up in a fir tree in British Columbia) that couldn’t be more different, yet are strikingly similar in their originality and brilliance. I started out my career heading into astrophysics, and I’m also an avid sea kayaker and I grew up with the B.C. rainforest out my back door. So I think I have a sense of what drives these guys. Yet I’ve never understood how Freeman Dyson became such a climate contrarian and advocate for off-the-wall biogeoengineering solutions like carbon-eating trees, something we’ve written about before.
One of my (Eric’s) favorite old books is The Starship and the Canoe by Kenneth Brower It’s a 1970s book about a father (Freeman Dyson, theoretical physicist living in Princeton) and son (George Dyson, hippy kayaker living 90 ft up in a fir tree in British Columbia) that couldn’t be more different, yet are strikingly similar in their originality and brilliance. I started out my career heading into astrophysics, and I’m also an avid sea kayaker and I grew up with the B.C. rainforest out my back door. So I think I have a sense of what drives these guys. Yet I’ve never understood how Freeman Dyson became such a climate contrarian and advocate for off-the-wall biogeoengineering solutions like carbon-eating trees, something we’ve written about before.
It turns out that Brower has wondered the same thing, and in a recent article in The Atlantic, he speculates on the answer. “How could someone as smart as Freeman Dyson,” writes Brower, “be so wrong about climate change and other environmental concerns..?”
[Read more…] about The Starship vs. Spaceship Earth
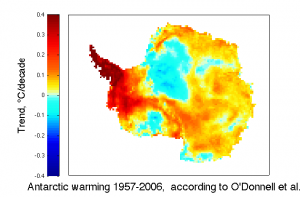
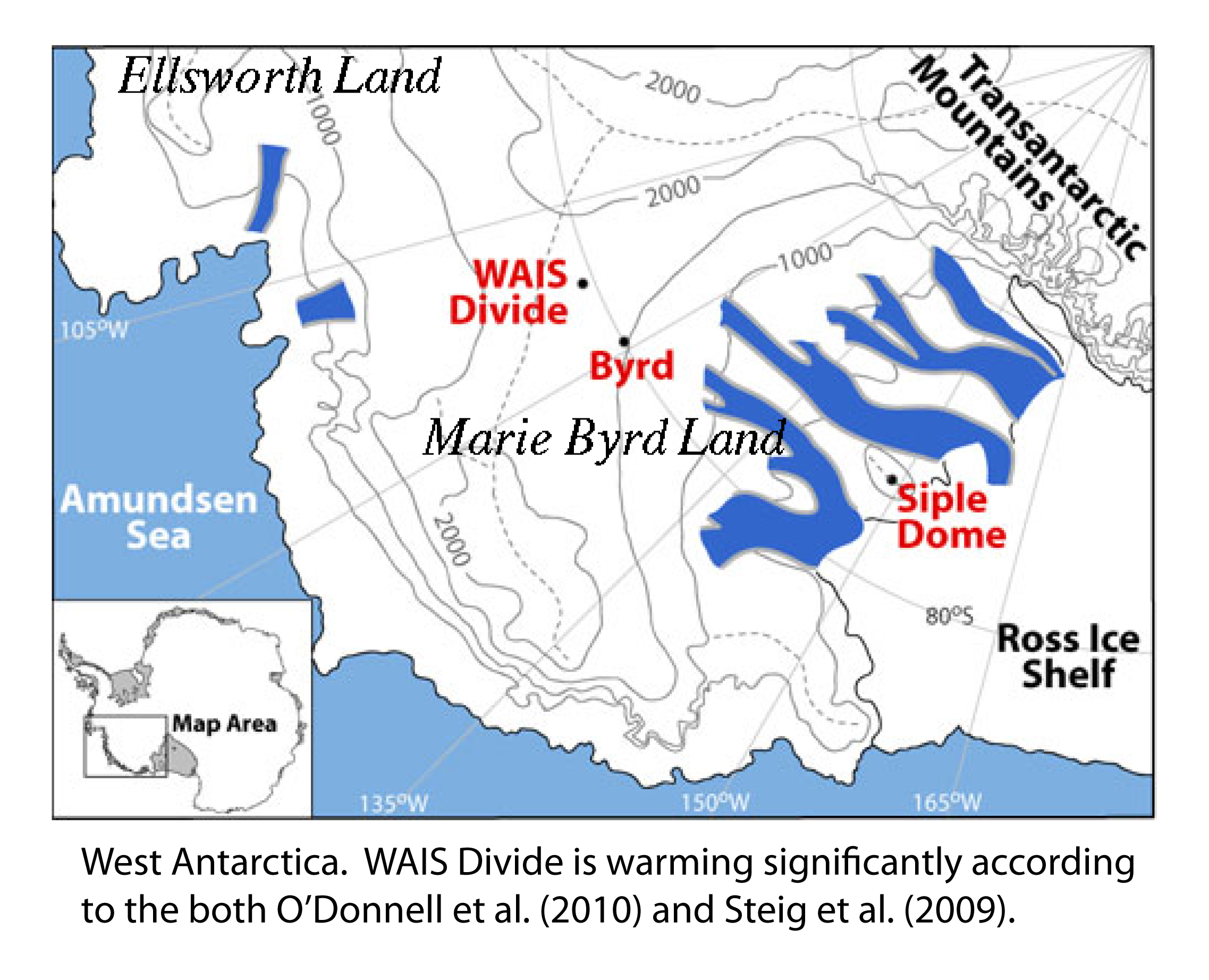 In this post, I’ll summarize the key methodological changes suggested by O’Donnell et al., discuss how their results compare with our results, and the implications for our understanding of recent Antarctic climate change. I’ll then try to make sense of how O’Donnell et al. have apparently wound up with an erroneous result.
In this post, I’ll summarize the key methodological changes suggested by O’Donnell et al., discuss how their results compare with our results, and the implications for our understanding of recent Antarctic climate change. I’ll then try to make sense of how O’Donnell et al. have apparently wound up with an erroneous result.