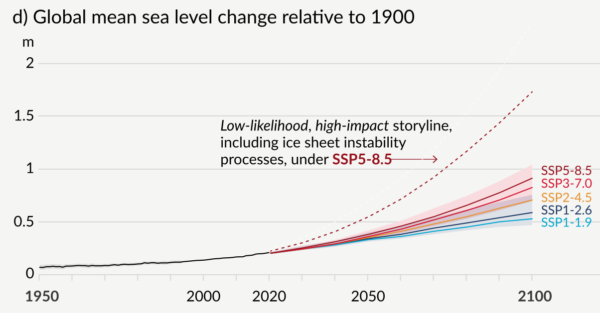
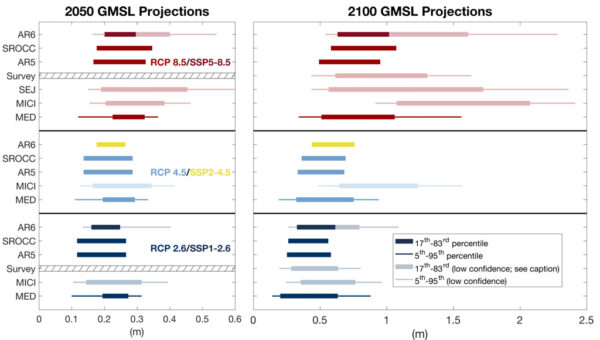
The CMIP6 multi-model ensemble is a unique resource with input from scientists and modeling groups from around the world. [CMIP stands for the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project, and it is now in its 6th Phase]. But as we’ve discussed before (#NotAllModels) there are some specific issues that require users to be cautious in making predictions. Fortunately, there are useful ‘best practices’ that can help avoid the worst pitfalls.
A new paper by McCrystall et al that has just appeared in Nature Communications illustrates these issues clearly by having some excellent analyses of the changes in Arctic precipitation regimes at different global warming levels, and examining the sensitivity of their metrics to both local and Arctic warming, but unfortunately relying on the CMIP6 multi-model mean for their headline statements and press release.
[Read more…] about Making predictions with the CMIP6 ensembleReferences
- M.R. McCrystall, J. Stroeve, M. Serreze, B.C. Forbes, and J.A. Screen, "New climate models reveal faster and larger increases in Arctic precipitation than previously projected", Nature Communications, vol. 12, 2021. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27031-y