Guest commentary by Kevin Trenberth and John Fasullo
The hype surrounding a new paper by Roy Spencer and Danny Braswell is impressive (see for instance Fox News); unfortunately the paper itself is not. News releases and blogs on climate denier web sites have publicized the claim from the paper’s news release that “Climate models get energy balance wrong, make too hot forecasts of global warming”. The paper has been published in a journal called Remote sensing which is a fine journal for geographers, but it does not deal with atmospheric and climate science, and it is evident that this paper did not get an adequate peer review. It should not have been published.
The paper’s title “On the Misdiagnosis of Surface Temperature Feedbacks from Variations in Earth’s Radiant Energy Balance” is provocative and should have raised red flags with the editors. The basic material in the paper has very basic shortcomings because no statistical significance of results, error bars or uncertainties are given either in the figures or discussed in the text. Moreover the description of methods of what was done is not sufficient to be able to replicate results. As a first step, some quick checks have been made to see whether results can be replicated and we find some points of contention.
The basic observational result seems to be similar to what we can produce but use of slightly different datasets, such as the EBAF CERES dataset, changes the results to be somewhat less in magnitude. And some parts of the results do appear to be significant. So are they replicated in climate models? Spencer and Braswell say no, but this is where attempts to replicate their results require clarification. In contrast, some model results do appear to fall well within the range of uncertainties of the observations. How can that be? For one, the observations cover a 10 year period. The models cover a hundred year period for the 20th century. The latter were detrended by Spencer but for the 20th century that should not be necessary. One could and perhaps should treat the 100 years as 10 sets of 10 years and see whether the observations match any of the ten year periods, but instead what appears to have been done is to use only the one hundred year set by itself. We have done exactly this and the result is in the Figure..
[ed. note: italics below replace the deleted sentence above, to make it clearer what is meant here.]
SB11 appears to have used the full 100 year record to evaluate the models, but this provides no indication of the robustness of their derived relationships. Here instead, we have considered each decade of the 20th century individually and quantified the inter-decadal variability to derive the Figure below. What this figure shows is the results for the observations, as in Spencer and Braswell, using the EBAF dataset (in black). Then we show results from 2 different models, one which does not replicate ENSO well (top) and one which does (second panel). Here we give the average result (red curve) for all 10 decades, plus the range of results that reflects the variations from one decade to the next. The MPI-Echam5 model replicates the observations very well. When all model results from CMIP3 are included, the bottom panel results, showing the red curve not too dis-similar from Spencer and Braswell, but with a huge range, due both to the spread among models, and also the spread due to decadal variability.
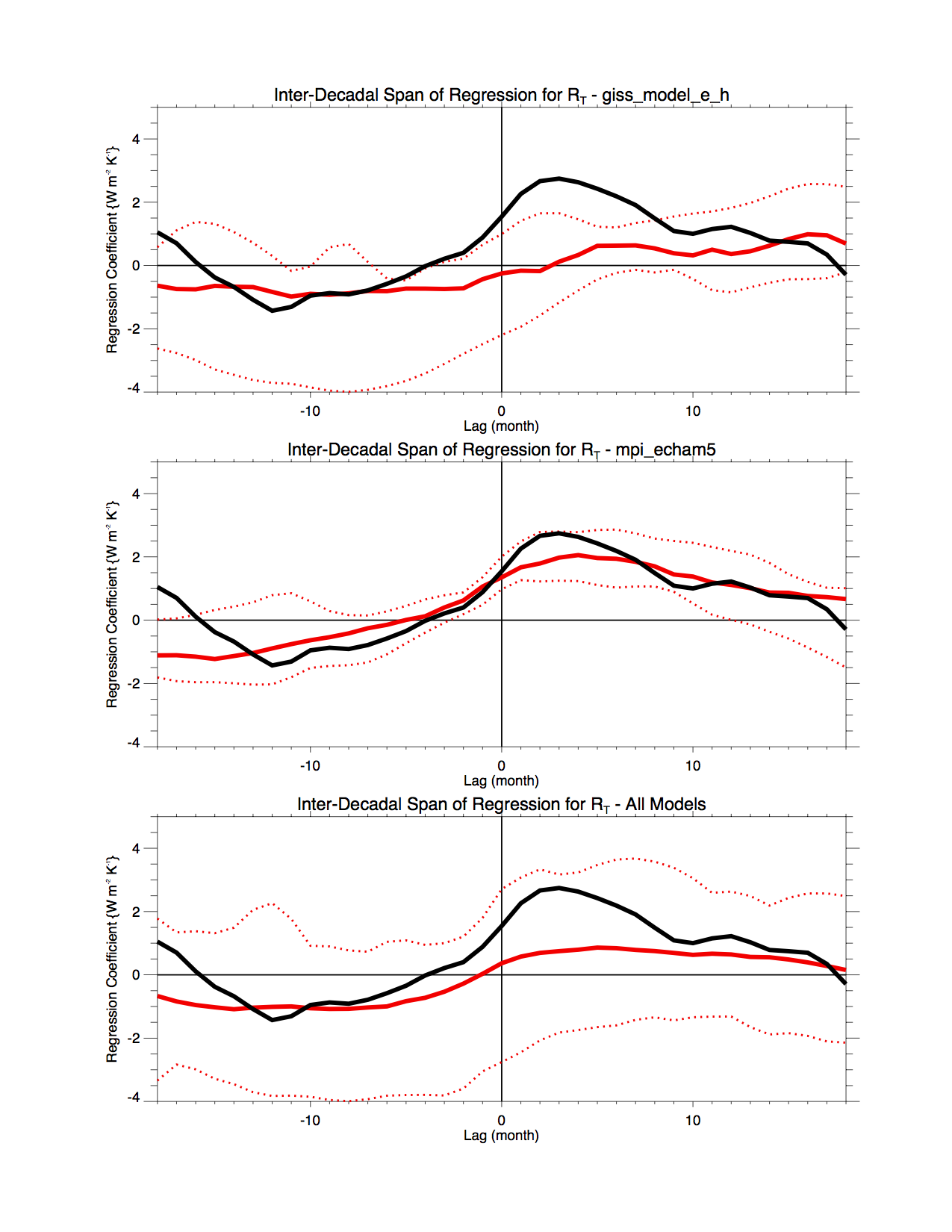
Figure: Lagged regression analysis for the Top-of-the-atmosphere Net Radiation against surface temperature. The CERES data is in black (as in SB11), and the individual models in each panel are in red. The dashed lines are the span of the regressions for specific 10 year periods in the model (so that the variance is comparable to the 10 years of the CERES data). The three panels show results for a) a model with poor ENSO variability, b) a model with reasonable ENSO variability, and c) all models.
Consequently, our results suggest that there are good models and some not so good, but rather than stratifying them by climate sensitivity, one should, in this case, stratify them by ability to simulate ENSO. In the Figure, the model that replicates the observations better has high sensitivity while the other has low sensitivity. The net result is that the models agree within reasonable bounds with the observations.
To help interpret the results, Spencer uses a simple model. But the simple model used by Spencer is too simple (Einstein says that things should be made as simple as possible but not simpler): well this has gone way beyond being too simple (see for instance this post by Barry Bickmore). The model has no realistic ocean, no El Niño, and no hydrological cycle, and it was tuned to give the result it gave. Most of what goes on in the real world of significance that causes the relationship in the paper is ENSO. We have already rebutted Lindzen’s work on exactly this point. The clouds respond to ENSO, not the other way round [see: Trenberth, K. E., J. T. Fasullo, C. O’Dell, and T. Wong, 2010: Relationships between tropical sea surface temperatures and top-of-atmosphere radiation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L03702, doi:10.1029/2009GL042314.] During ENSO there is a major uptake of heat by the ocean during the La Niña phase and the heat is moved around and stored in the ocean in the tropical western Pacific, setting the stage for the next El Niño, as which point it is redistributed across the tropical Pacific. The ocean cools as the atmosphere responds with characteristic El Niño weather patterns forced from the region that influence weather patterns world wide. Ocean dynamics play a major role in moving heat around, and atmosphere-ocean interaction is a key to the ENSO cycle. None of those processes are included in the Spencer model.
Even so, the Spencer interpretation has no merit. The interannual global temperature variations were not radiatively forced, as claimed for the 2000s, and therefore cannot be used to say anything about climate sensitivity. Clouds are not a forcing of the climate system (except for the small portion related to human related aerosol effects, which have a small effect on clouds). Clouds mainly occur because of weather systems (e.g., warm air rises and produces convection, and so on); they do not cause the weather systems. Clouds may provide feedbacks on the weather systems. Spencer has made this error of confounding forcing and feedback before and it leads to a misinterpretation of his results.
The bottom line is that there is NO merit whatsoever in this paper. It turns out that Spencer and Braswell have an almost perfect title for their paper: “the misdiagnosis of surface temperature feedbacks from variations in the Earth’s Radiant Energy Balance” (leaving out the “On”).



