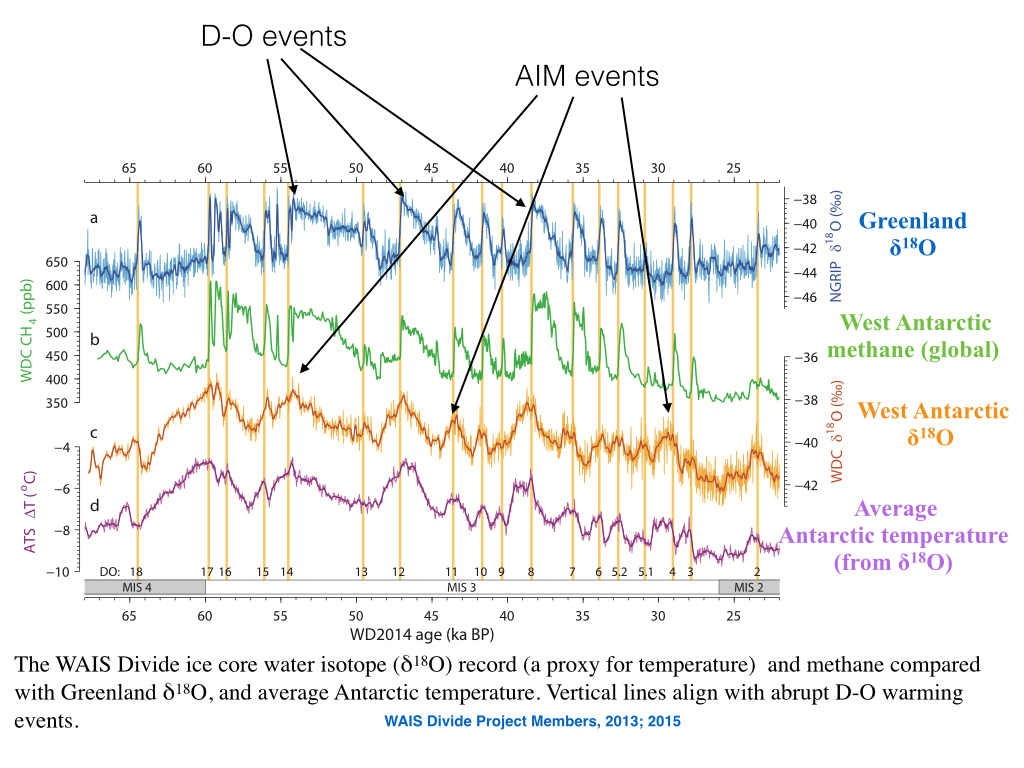
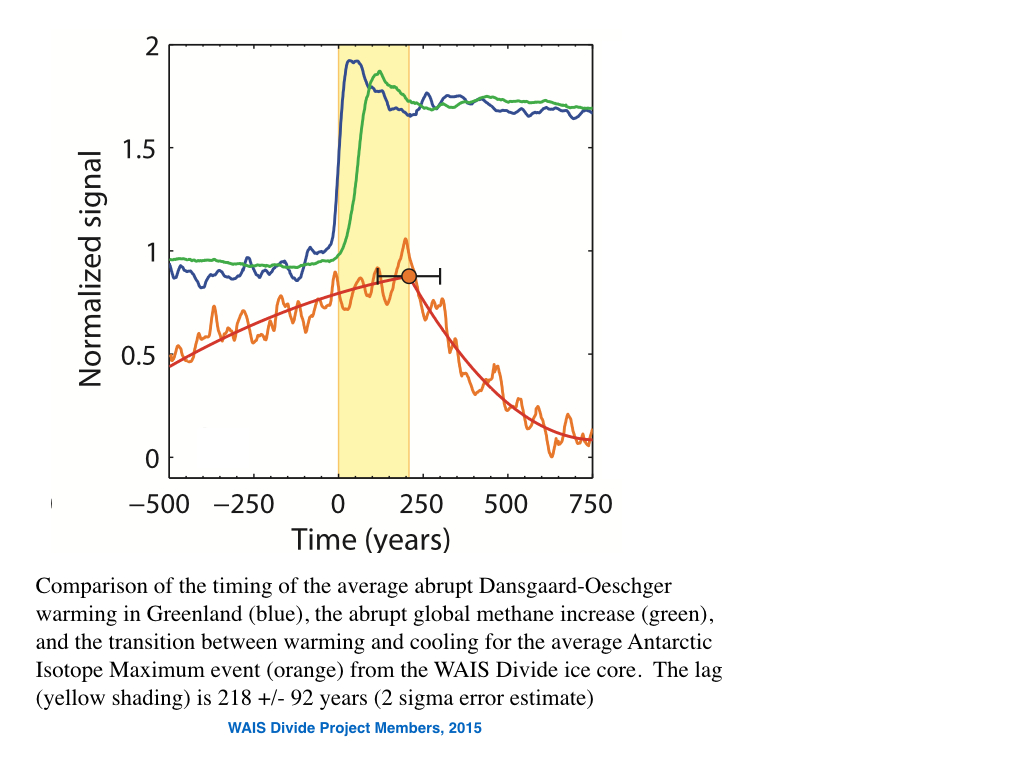
Guest commentary from Jonny McAneney
You heard it here first…
Back in February, we wrote a post suggesting that Greenland ice cores may have been incorrectly dated in prior to AD 1000. This was based on research by Baillie and McAneney (2015) which compared the spacing between frost ring events (physical scarring of living growth rings by prolonged sub-zero temperatures) in the bristlecone pine tree ring chronology, and spacing between prominent acids in a suite of ice cores from both Greenland and Antarctica. The main conclusion was that ice core dates, in particular those ice cores relied upon the Greenland Ice Core Chronology 2005 (GICC05), such as the NEEM S1 core, were too old by approximately seven years during the 6th and 7th centuries AD.
Last month, in an excellent piece of research (Sigl et al., 2015) by a collaboration including Earth scientists, dendrochonologists, and historians, the chronology of the Greenland North Eemian Ice Drilling core (NEEM) has been reassessed and re-dated, confirming that such an offset does indeed exist in the GICC05 timescale below AD 1000. The clinching evidence was provided by linking tree-ring chronologies to ice cores through two extraterrestrial events…
[Read more…] about Ice-core dating corroborates tree ring chronologies
References
- M.G.L. Baillie, and J. McAneney, "Tree ring effects and ice core acidities clarify the volcanic record of the first millennium", Climate of the Past, vol. 11, pp. 105-114, 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.5194/cp-11-105-2015
- B.M. Vinther, H.B. Clausen, S.J. Johnsen, S.O. Rasmussen, K.K. Andersen, S.L. Buchardt, D. Dahl‐Jensen, I.K. Seierstad, M. Siggaard‐Andersen, J.P. Steffensen, A. Svensson, J. Olsen, and J. Heinemeier, "A synchronized dating of three Greenland ice cores throughout the Holocene", Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, vol. 111, 2006. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2005JD006921
- M. Sigl, J.R. McConnell, L. Layman, O. Maselli, K. McGwire, D. Pasteris, D. Dahl‐Jensen, J.P. Steffensen, B. Vinther, R. Edwards, R. Mulvaney, and S. Kipfstuhl, "A new bipolar ice core record of volcanism from WAIS Divide and NEEM and implications for climate forcing of the last 2000 years", Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, vol. 118, pp. 1151-1169, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2012JD018603
- M. Sigl, M. Winstrup, J.R. McConnell, K.C. Welten, G. Plunkett, F. Ludlow, U. Büntgen, M. Caffee, N. Chellman, D. Dahl-Jensen, H. Fischer, S. Kipfstuhl, C. Kostick, O.J. Maselli, F. Mekhaldi, R. Mulvaney, R. Muscheler, D.R. Pasteris, J.R. Pilcher, M. Salzer, S. Schüpbach, J.P. Steffensen, B.M. Vinther, and T.E. Woodruff, "Timing and climate forcing of volcanic eruptions for the past 2,500 years", Nature, vol. 523, pp. 543-549, 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14565