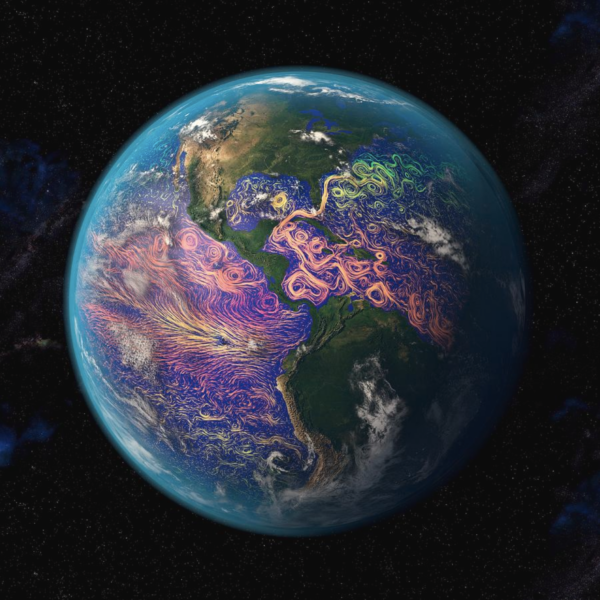
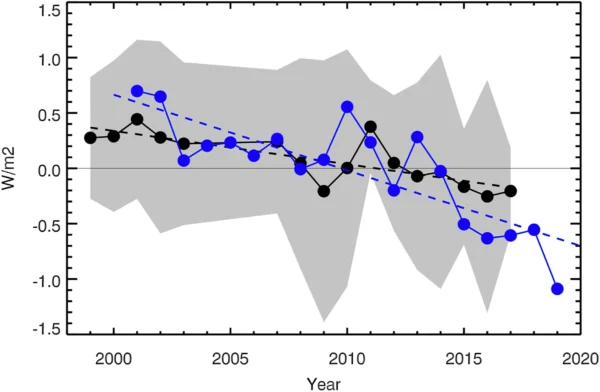
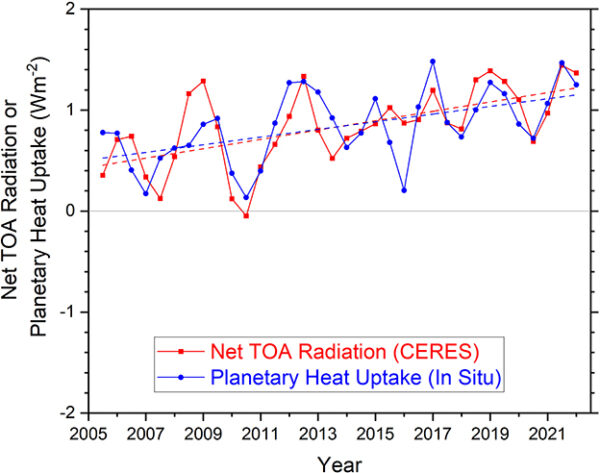
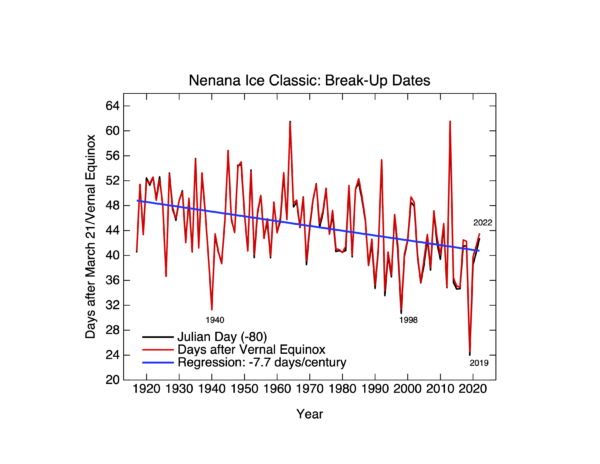
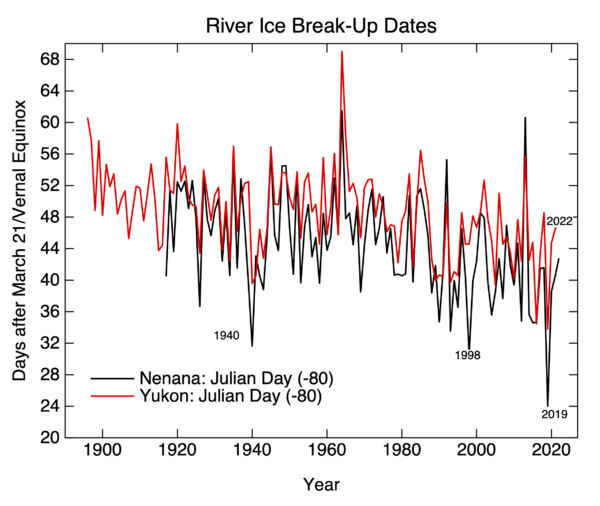
The detection and the attribution of climate change are based on fundamentally different frameworks and shouldn’t be conflated.
We read about and use the phrase ‘detection and attribution’ of climate change so often that it seems like it’s just one word ‘detectionandattribution’ and that might lead some to think that it is just one concept. But it’s not.
[Read more…] about Watching the detections