Guest Commentary by Cristian Proistosescu, Peter Huybers and Kyle Armour
tl;dr
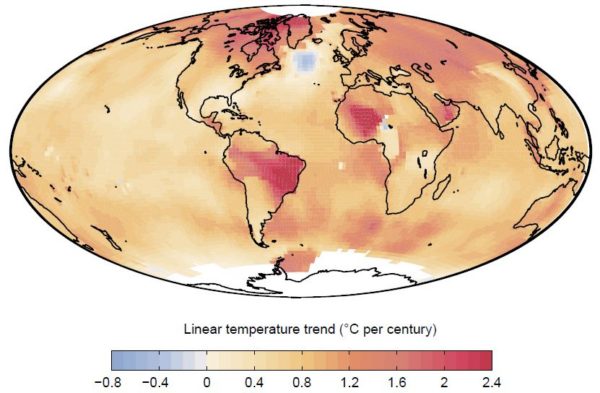
Two recent papers help bridge a seeming gap between estimates of climate sensitivity from models and from observations of the global energy budget. Recognizing that equilibrium climate sensitivity cannot be directly observed because Earth’s energy balance is a long way from equilibrium, the studies instead focus on what can be inferred about climate sensitivity from historical trends. Calculating a climate sensitivity from the simulations that is directly comparable with that observed shows both are consistent. Crucial questions remain, however, regarding how climate sensitivity will evolve in the future.
[Read more…] about Sensible Questions on Climate Sensitivity