This month’s open thread… Expect pre-IPCC report discussion (SPM due on Sep 27, full report (pre-copy-editing) Sep 30th), analysis of this years Arctic ice cover minimum, and a host of the usual distractions.
Climate Science
The inevitability of sea level rise
Guest post by Anders Levermann [via The Conversation]
![]()
Small numbers can imply big things. Global sea level rose by a little less than 0.2 metres during the 20th century – mainly in response to the 0.8 °C of warming humans have caused through greenhouse gas emissions. That might not look like something to worry about. But there is no doubt that for the next century, sea level will continue to rise substantially. The multi-billion-dollar question is: by how much? [Read more…] about The inevitability of sea level rise
Unforced variations: August 2013
This month’s open thread.
Since there are two main topics (Advocacy and Methane bombs) buzzing around the blogo-twitter-sphere this week, perhaps those are our starters for ten… (Feel free to populate the comments with links to various commentaries – we will chime in as we find time).
Arctic misrepresentations
At the weekend, Christopher Booker at the Daily Telegraph made another attempt (see previous) to downplay the obvious decreases in Arctic sea ice by (mis-)quoting a statement from Arctic oceanographer Ken Drinkwater and colleagues:
[Read more…] about Arctic misrepresentations
AGU Chapman Conference on Climate Science Communication
A couple of weeks ago, there was a small conference on Climate Science communication run by the AGU. Both Mike and I attended, but it was very notable that it wasn’t just scientists attending – there were also entertainers, psychologists, film-makers and historians. There were a lot of quite diverse perspectives and many discussions about the what’s, why’s and how’s of climate science communication.
There were a couple of notable features: the conference had a lively twitter hashtag (#climatechapman), and almost the entire proceedings were webcast live (schedule). The video from this has now been posted on YouTube in more bite-sized chunks.
While our own presentations (Mike here and Gavin here) are available, it is worth watching the presentations from people you might not have heard of, as well as a few from more established people. We’ll embed a few here, but please point out some of the other ones of interest in the comments.
[Read more…] about AGU Chapman Conference on Climate Science Communication
Unforced Variations: July 2013
This month’s open thread…
We have just updated the blog software, and are taking a little time to assess how up-to-date some the content is (including the theme, mobile theme, blogroll, about pages and the RC wiki etc.). So this might be a good time to chime in with your suggestions as well as discussing the latest climate science issues.
A new experiment with science publication
A while ago, I received a request to publish a paper on a post that I had written here on RealClimate, exposing the flaws in the analysis of Humlum et al., (2011).
Instead of writing a comment to one paper, however, I thought it might be useful to collect a sample of papers that I found unconvincing (usual suspects), and that have had a fairly high public profile.
[Read more…] about A new experiment with science publication
References
- O. Humlum, J. Solheim, and K. Stordahl, "Identifying natural contributions to late Holocene climate change", Global and Planetary Change, vol. 79, pp. 145-156, 2011. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2011.09.005
Yamal and Polar Urals: a research update
Guest commentary from Tim Osborn, Tom Melvin and Keith Briffa, Climatic Research Unit, UEA
Records of tree-ring characteristics such as their width (TRW) and density (usually the maximum density of the wood formed towards the end of the growing season – the “maximum latewood density” – MXD) are widely used to infer past variations in climate over recent centuries and even millennia. Chronologies developed from sites near to the elevational or latitudinal tree lines often show sensitivity to summer temperature and, because of their annual resolution, absolute dating and relatively widespread nature, they have contributed to many local, continental and hemispheric temperature reconstructions. However, tree growth is a complex biological process that is subject to a range of changing environmental influences, not just summer temperature, and so replication, coherence and consistency across records and other proxies are an important check on the results.
Tree-ring records have greater replication (both within a site and between nearby sites) than other types of climate proxy. Good replication helps to minimise the influence of random localised factors when extracting the common signal, and it also allows the comparison of information obtained from different independent sets or sub-sets of data. If independent sets of data – perhaps trees with different mean growth rates or from different sites – show similar variations, then we can have greater confidence that those variations are linked to real variations in climate.
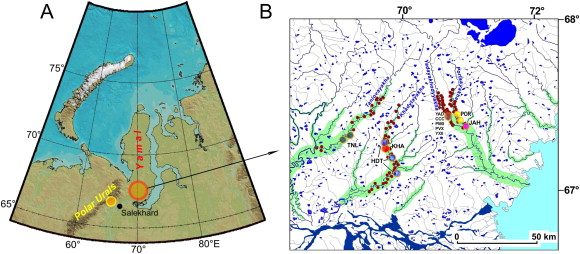
In a new QSR paper (Briffa et al., 2013), (BEA13) we have used these approaches to re-assess the combined tree-ring evidence from the Yamal and Polar Urals region (Yamalia) of northern Siberia, considering the common signal in tree-growth changes at different sites and in subsets of data defined in other ways. Together with our Russian colleagues and co-authors, we have incorporated many new tree-ring data, to increase the replication and to update the chronology to 2005 and have reassessed the inferences about summer temperature change that can be drawn from these data. The paper is published as an open-access paper (no paywall) and supplementary information including the raw tree-ring and instrumental temperature data are available from our website.
[Read more…] about Yamal and Polar Urals: a research update
References
- K.R. Briffa, T.M. Melvin, T.J. Osborn, R.M. Hantemirov, A.V. Kirdyanov, V.S. Mazepa, S.G. Shiyatov, and J. Esper, "Reassessing the evidence for tree-growth and inferred temperature change during the Common Era in Yamalia, northwest Siberia", Quaternary Science Reviews, vol. 72, pp. 83-107, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.04.008