Much of the discussion in recent days has been motivated by the idea that climate science is somehow unfairly restricting access to raw data upon which scientific conclusions are based. This is a powerful meme and one that has clear resonance far beyond the people who are actually interested in analysing data themselves. However, many of the people raising this issue are not aware of what and how much data is actually available.
Therefore, we have set up a page of data links to sources of temperature and other climate data, codes to process it, model outputs, model codes, reconstructions, paleo-records, the codes involved in reconstructions etc. We have made a start on this on a new Data Sources page, but if anyone has other links that we’ve missed, note them in the comments and we’ll update accordingly.
The climate science community fully understands how important it is that data sources are made as open and transparent as possible, for research purposes as well as for other interested parties, and is actively working to increase accessibility and usability of the data. We encourage people to investigate the various graphical portals to get a feel for the data and what can be done with it. The providers of these online resources are very interested in getting feedback on any of these sites and so don’t hesitate to contact them if you want to see improvements.
Update: Big thank you to all for all the additional links given below. Keep them coming!

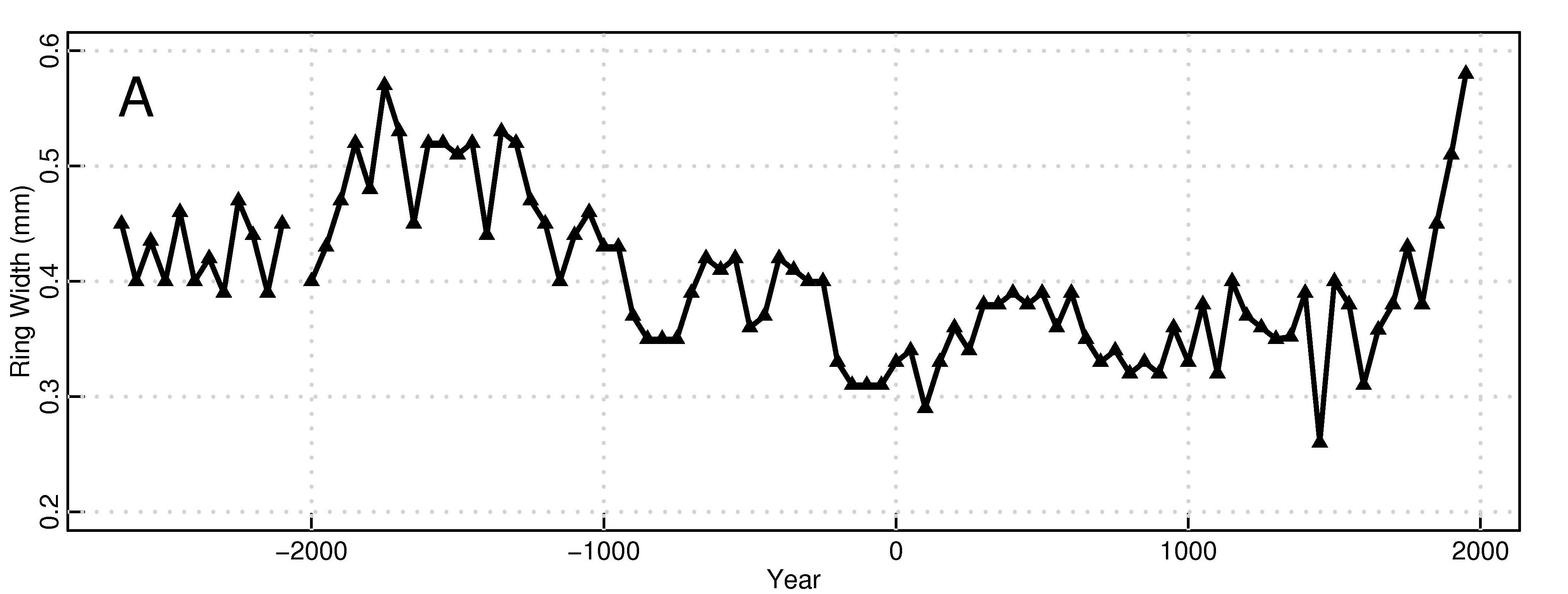
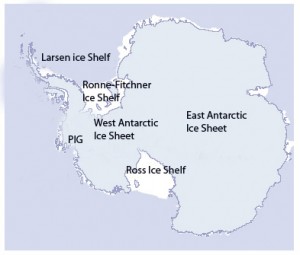 It is popularly understood that glaciologists consider West Antarctica the biggest source of uncertainty in sea level projections. The base of the 3000-m thick West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) – unlike the much larger East Antarctic Ice Sheet – lies below sea level, and it has been recognized for a long time that this means it has the potential to change very rapidly. Most of the grounded West Antarctic ice sheet drains into the floating Ross and Ronne-Filchner ice shelves, but a significant fraction also drains into the much smaller Pine Island Glacier. Glaciologists are paying very close attention to Pine Island Glacier (“PIG” on map, right) and nearby Thwaites Glacier. In the following guest post, Mauri Pelto explains why.
It is popularly understood that glaciologists consider West Antarctica the biggest source of uncertainty in sea level projections. The base of the 3000-m thick West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) – unlike the much larger East Antarctic Ice Sheet – lies below sea level, and it has been recognized for a long time that this means it has the potential to change very rapidly. Most of the grounded West Antarctic ice sheet drains into the floating Ross and Ronne-Filchner ice shelves, but a significant fraction also drains into the much smaller Pine Island Glacier. Glaciologists are paying very close attention to Pine Island Glacier (“PIG” on map, right) and nearby Thwaites Glacier. In the following guest post, Mauri Pelto explains why.