While there have been some recent set-backs within science and climate research and disturbing news about NOAA, there is also continuing efforts on responding to climate change. During my travels to Mozambique and Ghana, I could sense a real appreciation for knowledge, and an eagerness to learn how to calculate risks connected to climate change.
[Read more…] about Climate change in AfricaClimate impacts
Operationalizing Climate Science
There is a need to make climate science more agile and more responsive, and that means moving (some of it) from research to operations.
[Read more…] about Operationalizing Climate Science2023 appears to follow an upward trend in the North Atlantic/Caribbean named tropical cyclone count
This year’s (2023) tropical cyclone season in the North Atlantic and Caribbean witnessed a relatively high number of named tropical cyclones: 20. In spite of the current El Niño, which tends to give lower numbers. But it appears to follow a historical trend for named tropical cyclones with an increasing number over time.
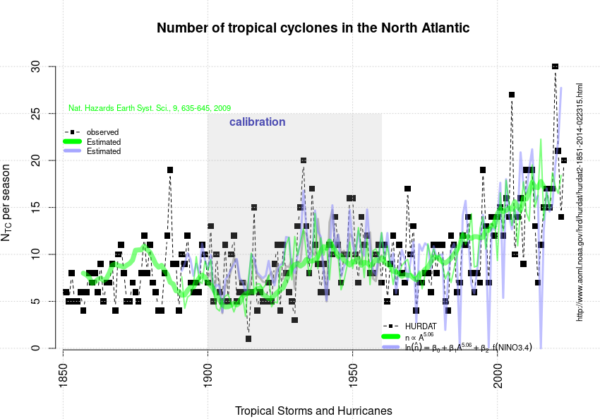
The curve presented above is an update of the analysis presented in 2020 and posted here on RealClimate.
[Read more…] about 2023 appears to follow an upward trend in the North Atlantic/Caribbean named tropical cyclone countReferences
- R.E. Benestad, "On tropical cyclone frequency and the warm pool area", Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, vol. 9, pp. 635-645, 2009. http://dx.doi.org/10.5194/nhess-9-635-2009
Unforced variations: Sep 2023
This month’s open thread on climate science topics. It’s been a warm summer, dontcha know? Expect ERA5, the satellite data and then the surface data products to confirm this in the next week or so. Sea ice minimum in the Arctic will also occur soon, as will a record low maximum in the Antarctic. El Niño still building in the tropical Pacific. Interesting times…
What is happening in the Atlantic Ocean to the AMOC?
For various reasons I’m motivated to provide an update on my current thinking regarding the slowdown and tipping point of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC). I attended a two-day AMOC session at the IUGG Conference the week before last, there’s been interesting new papers, and in the light of that I have been changing my views somewhat. Here’s ten points, starting from the very basics, so you can easily jump to the aspects that interest you.
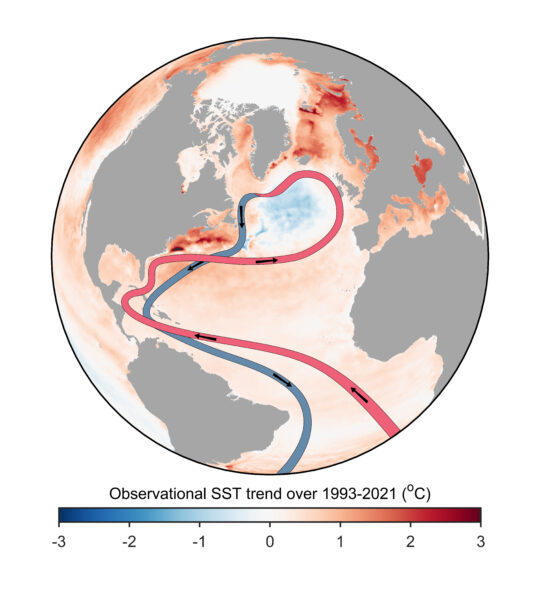
Back to basics
You can tell how worried the climate deniers are by how many fields of science they have to trash to try and have people not see what’s happening.
it will not have escaped most people’s notice that global temperatures are heading into uncharted territory. The proximate cause of this week’s headlines is the Climate Reanalyzer website at the U. Maine which provides a nice front end to the NOAA NCEP CFS forecast system and reanalysis and shows absolute daily temperatures in early July clearly exceeding the highest pre-existing temperatures from August 2016. It’s an arresting graphic, and follows in from the record high ocean surface temperatures that were being reported a month ago.
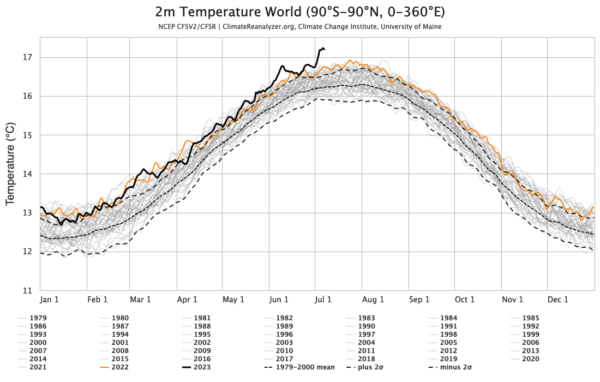
This is however a relatively new resource and was not online the last time that we set absolute temperature records (in summer 2016). So this has both salience and novelty – a potent combination!
The ultimate cause of these patterns is of course the ongoing global warming, driven almost entirely by human activities.
What are we looking at?
As we’ve explained before, all global temperature products are based on some kind of model – statistical, physical etc. There is no direct measurement of the global temperature – not from satellites, stations, or from the one random person who happens to be in most average place on Earth (where might that even be?). But that doesn’t mean the products aren’t useful!
In this particular instance we are looking at the output of a weather forecast model (NCEP CFS) that ingests multiple sources of in situ and satellite data every 3 hours which is then averaged over a day and over the surface of the planet. These calculations are precise reflections of what is in the model, but for multiple reasons this might not be a perfect reflection of what the real world is doing.
We looked at the coherence of different products, including the reanalyses, before and found that while they are highly correlated in terms of annual anomalies, they differ in their absolute magnitude (graphic from 2017).
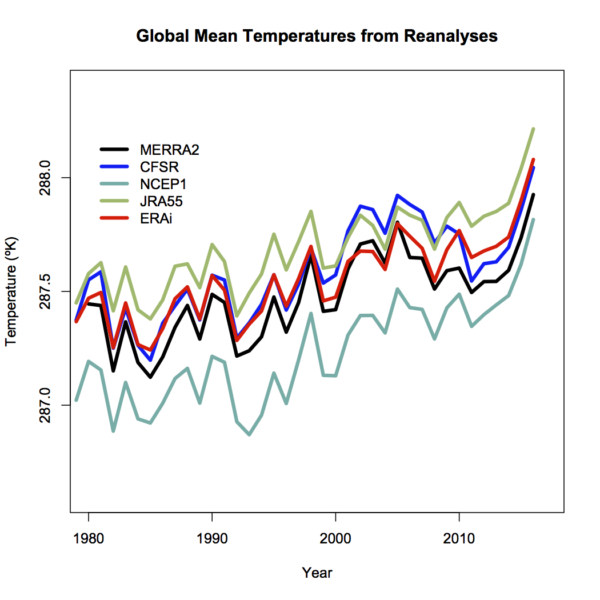
Differences will depend on resolution – higher resolution models have better (and higher topography) and then will have slightly cooler temperatures (all else being equal – which it isn’t!), tuning, model structure etc. and can’t really be discriminated using the pure (sparse) observations.
Coherence at the monthly scale is also quite good (though a little noisier), and I haven’t (yet) seen a good comparison of the coherence of the different products at the daily scale (note that the standard products (like GISTEMP, HadCRUT5 and NOAAv5) don’t produce a daily product). One might anticipate that there is a similarity, but perhaps not a one-to-one correspondence on exactly which days were the warmest.
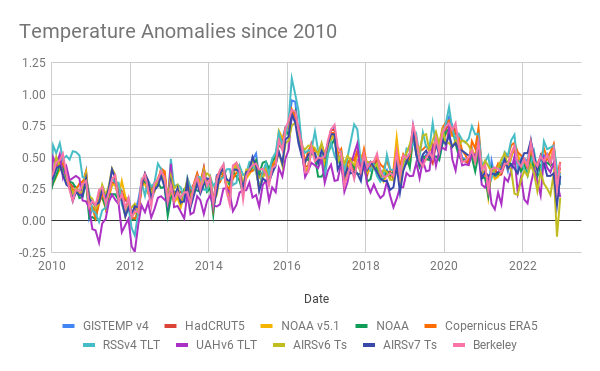
What are we seeing?
For the global temperature, it’s well established that the maximum is during the Northern Hemisphere summer. This sometimes comes as a surprise to people (why doesn’t the opposing seasonality in the Southern Hemisphere cancel this out?), but it relates to the fact that there is a lot more land in the Northern Hemisphere. Since the seasonal cycle over land is much larger than over the ocean (smaller heat capacity, and less evaporation), that means that the seasonal variations in the north outweigh the variations in the south.
Thus the months of July and August are generally the warmest in the year, and consequently we expect the warmest days during those months – and this is reflected in the CFS output (and in the ERA5 output also). The monthly variations are also reflected in the GISTEMP product which allows you to see the shifts from 1880 onward (about a 1ºC warming in each month since the late 19th C):
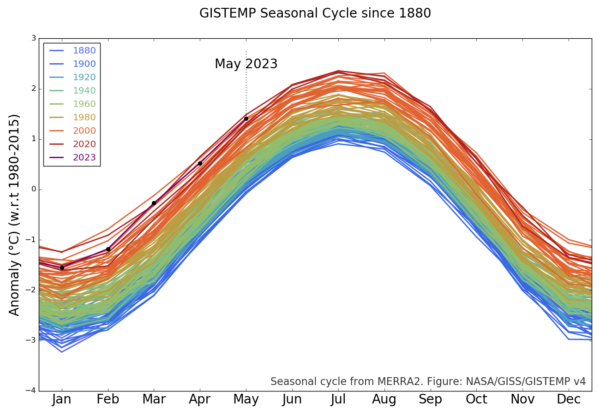
The station-based products are a little delayed with respect to the reanalyses, but they generally reflect the same patterns – thus one should expect the June temperatures in NOAA, GISTEMP and HadCRUT5 to be the warmest June on record. Given too, that these temperatures are being driven by persistent warming in the oceans, increasingly juiced by the growing El Niño event in the tropical Pacific, records in July and August are also likely. This is of course increasing the odds for 2023 to be a record year (I would estimate about 50% at this point).
But the WSJ Opinion page says that there’s no such thing as the global temperature!
Well, they would say that wouldn’t they. [Narrator: there is, in fact, a perfectly well defined global mean of any two-dimensional field defined on the sphere, including temperature].
More generously, one might think that their argument (such as it is), is that the global mean isn’t directly relevant for anyone. That is, no-one lives in the global mean, all impacts are local and driven by weather variations. But we’ve known for decades that the global mean change is a really good predictor (not perfect, but pretty good) of local impacts on heat waves, intense rainfall, drought intensity etc.
But let’s be honest, it’s basically pure distraction and attempts to complicate something that is pretty basic:
The climate is warming, records are being broken, and we are increasingly seeing the impacts.
I know why the WSJ doesn’t want you to realise this, but it’s not hard to see past their obfuscation.
Turning a new page[s]
The world is full of climate dashboards (and dashboards of dashboards), and so you might imagine that all datasets and comparisons are instantly available in whatever graphical form you like. Unfortunately, we often want graphics to emphasize a particular point or comparison, and generic graphs from the producers of the data often don’t have the same goal in mind. Dashboards that allow for more flexibility (like WoodForTrees) are useful, but aren’t as visually appealing as they could be. Thus, I find myself creating bespoke graphics of climate and climate model data all the time.
Some of these are maintained on the Climate model-observations comparison page but many of the graphs that I make (often to make a point on twitter) aren’t saved there and often their provenance is a bit obscure. Given that twitter will not last forever (though it might be around for slightly longer than a head of lettuce), it’s probably useful to have a spot to upload these graphics to, along with some explanation, to serve as a reference.
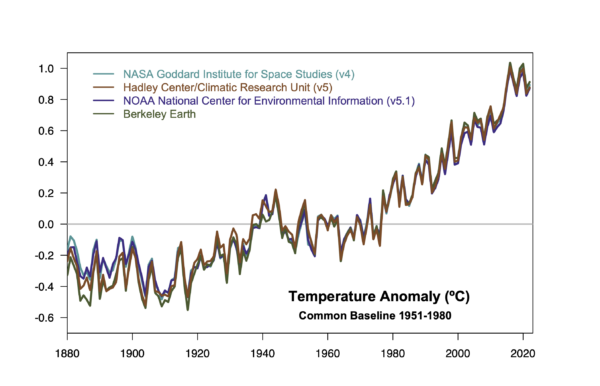
I have therefore created a couple of ‘pages’ (in wordpress speak) with fixed URLs where I will be curating relevant graphics I make (and findable at the bottom of the page under “DATA AND GRAPHICS”). The first is focused on the surface temperature records. I often update relevant graphics associated with this in early January (when we get another dot on the graphs), but there are associated graphs that I’ve made that don’t make it into those updates, so this is a place for them too. This includes the impacts of ENSO, comparisons across different platforms, or the impact of homogenization.
The second page is bit more eclectic. These are graphs that are relevant to some trope or talking point that often pops up, and my graphs are an attempt to provide context (usually), or to debunk it entirely. This is where you’ll find maps of where the climate is warming faster than the global average, time-series of river ice break-up dates, and an example of sensible scaling of CO2 changes and temperature.
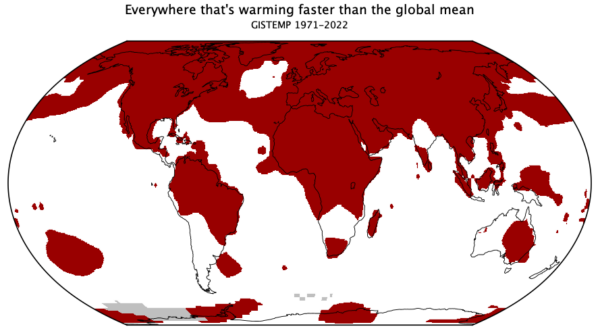
To start with, I’m just going to upload some graphs I’ve made recently (with any updates that are needed), and I’ll add content as I make something new. If there are any other ideas (that aren’t too involved!), I’ll be happy to look at adding those too. Let me know if this is useful.
Watching the detections
The detection and the attribution of climate change are based on fundamentally different frameworks and shouldn’t be conflated.
We read about and use the phrase ‘detection and attribution’ of climate change so often that it seems like it’s just one word ‘detectionandattribution’ and that might lead some to think that it is just one concept. But it’s not.
[Read more…] about Watching the detectionsClimate impacts of the #IRA
With the signing of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) on Tuesday Aug 16, the most significant climate legislation in US federal history (so far) became law.

Despite the odd name (and greatly overused TLA), the IRA contains a huge number of elements, totalling roughly $350 billion of investment, in climate solutions over the next ten years. This is an historic effort though it falls short of the broader ‘Green New Deal‘ goals that were proposed in 2019, and doesn’t include all of the elements that were in the proposed 2021 reconcilliation package (the American Jobs Plan in “Build Back Better“) that ultimately floundered.
[Read more…] about Climate impacts of the #IRAThe CO2 problem in six easy steps (2022 Update)
One of our most-read old posts is the step-by-step explanation for why increasing CO2 is a significant problem (The CO2 problem in 6 easy steps). However, that was written in 2007 – 15 years ago! While the basic steps and concepts have not changed, there’s 15 years of more data, updates in some of the details and concepts, and (it turns out) better graphics to accompany the text. And so, here is a mildly updated and referenced version that should be a little more useful.
[Read more…] about The CO2 problem in six easy steps (2022 Update)