Can a rising sea level can act as a boost for glaciers calving into the sea and trigger a surge of ice into the oceans? I finally got round to watch the documentary Chasing Ice over the Christmas and New Year’s break, and it made a big impression. I also was left with this question after watching it.
Arctic and Antarctic
Millennia of sea-level change
How has global sea level changed in the past millennia? And how will it change in this century and in the coming millennia? What part do humans play? Several new papers provide new insights.
2500 years of past sea level variations
This week, a paper will appear in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) with the first global statistical analysis of numerous individual studies of the history of sea level over the last 2500 years (Kopp et al. 2016 – I am one of the authors). Such data on past sea level changes before the start of tide gauge measurements can be obtained from drill cores in coastal sediments. By now there are enough local data curves from different parts of the world to create a global sea level curve.
Let’s right away look at the main result. The new global sea level history looks like this:
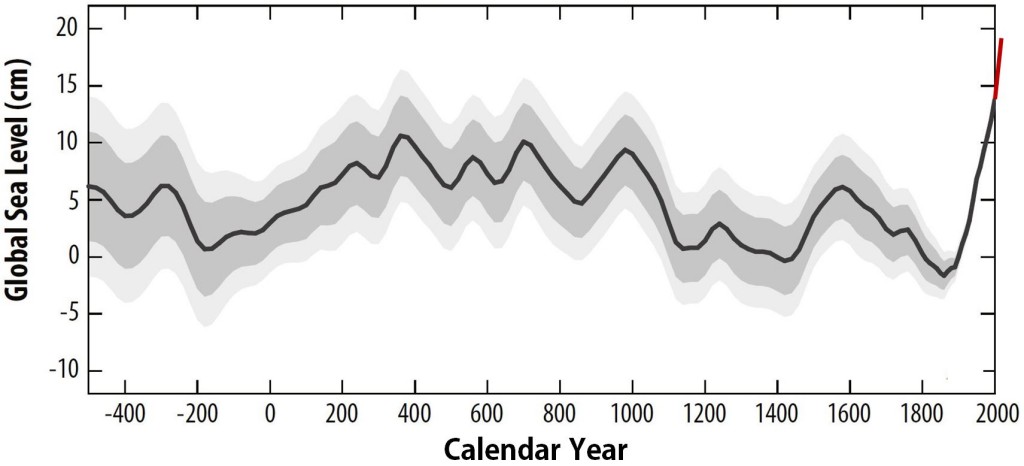
Fig. 1 Reconstruction of the global sea-level evolution based on proxy data from different parts of the world. The red line at the end (not included in the paper) illustrates the further global increase since 2000 by 5-6 cm from satellite data. [Read more…] about Millennia of sea-level change
References
- R.E. Kopp, A.C. Kemp, K. Bittermann, B.P. Horton, J.P. Donnelly, W.R. Gehrels, C.C. Hay, J.X. Mitrovica, E.D. Morrow, and S. Rahmstorf, "Temperature-driven global sea-level variability in the Common Era", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 113, 2016. http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1517056113
How much methane came out of that hole in Siberia?
Siberia has explosion holes in it that smell like methane, and there are newly found bubbles of methane in the Arctic Ocean. As a result, journalists are contacting me assuming that the Arctic Methane Apocalypse has begun. However, as a climate scientist I remain much more concerned about the fossil fuel industry than I am about Arctic methane. Short answer: It would take about 20,000,000 such eruptions within a few years to generate the standard Arctic Methane Apocalypse that people have been talking about. Here’s where that statement comes from:
[Read more…] about How much methane came out of that hole in Siberia?
Rossby waves and surface weather extremes
A new study by Screen and Simmonds demonstrates the statistical connection between high-amplitude planetary waves in the atmosphere and extreme weather events on the ground.
Guest post by Dim Coumou
There has been an ongoing debate, both in and outside the scientific community, whether rapid climate change in the Arctic might affect circulation patterns in the mid-latitudes, and thereby possibly the frequency or intensity of extreme weather events. The Arctic has been warming much faster than the rest of the globe (about twice the rate), associated with a rapid decline in sea-ice extent. If parts of the world warm faster than others then of course gradients in the horizontal temperature distribution will change – in this case the equator-to-pole gradient – which then could affect large scale wind patterns.
Several dynamical mechanisms for this have been proposed recently. Francis and Vavrus (GRL 2012) argued that a reduction of the north-south temperature gradient would cause weaker zonal winds (winds blowing west to east) and therefore a slower eastward propagation of Rossby waves. A change in Rossby wave propagation has not yet been detected (Barnes 2013) but this does not mean that it will not change in the future. Slowly-traveling waves (or quasi-stationary waves) would lead to more persistent and therefore more extreme weather. Petoukhov et al (2013) actually showed that several recent high-impact extremes, both heat waves and flooding events, were associated with high-amplitude quasi-stationary waves. [Read more…] about Rossby waves and surface weather extremes
References
- J.A. Francis, and S.J. Vavrus, "Evidence linking Arctic amplification to extreme weather in mid‐latitudes", Geophysical Research Letters, vol. 39, 2012. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2012GL051000
- E.A. Barnes, "Revisiting the evidence linking Arctic amplification to extreme weather in midlatitudes", Geophysical Research Letters, vol. 40, pp. 4734-4739, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/grl.50880
- V. Petoukhov, S. Rahmstorf, S. Petri, and H.J. Schellnhuber, "Quasiresonant amplification of planetary waves and recent Northern Hemisphere weather extremes", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 110, pp. 5336-5341, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1222000110
Faking it
Every so often contrarians post old newspaper quotes with the implication that nothing being talked about now is unprecedented or even unusual. And frankly, there are lots of old articles that get things wrong, are sensationalist or made predictions without a solid basis. And those are just the articles about the economy.
However, there are plenty of science articles that are just interesting, reporting events and explorations in the Arctic and elsewhere that give a fascinating view into how early scientists were coming to an understanding about climate change and processes. In particular, in the Atlantic sector of the Arctic the summer of 1922 was (for the time) quite warm, and there were a number of reports that discussed some unprecedented (again, for the time) observations of open water. The most detailed report was in the Monthly Weather Review:
[Read more…] about Faking it
Arctic and American Methane in Context
Lots of interesting methane papers this week. In Nature Geoscience, Shakhova et al (2013) have published a substantial new study of the methane cycle on the Siberian continental margin of the Arctic Ocean. This paper will get a lot of attention, because it follows by a few months a paper from last summer, Whiteman et al (2013), which claimed a strong (and expensive) potential impact from Arctic methane on near-term climate evolution. That economic modeling study was based on an Arctic methane release scenario proposed in an earlier paper by Shakhova (2010). In PNAS, Miller et al (2013) find that the United States may be emitting 50-70% more methane than we thought. So where does this leave us?
[Read more…] about Arctic and American Methane in Context
References
- N. Shakhova, I. Semiletov, I. Leifer, V. Sergienko, A. Salyuk, D. Kosmach, D. Chernykh, C. Stubbs, D. Nicolsky, V. Tumskoy, and �. Gustafsson, "Ebullition and storm-induced methane release from the East Siberian Arctic Shelf", Nature Geoscience, vol. 7, pp. 64-70, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/NGEO2007
- G. Whiteman, C. Hope, and P. Wadhams, "Vast costs of Arctic change", Nature, vol. 499, pp. 401-403, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/499401a
- N.E. Shakhova, V.A. Alekseev, and I.P. Semiletov, "Predicted methane emission on the East Siberian shelf", Doklady Earth Sciences, vol. 430, pp. 190-193, 2010. http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X10020091
- S.M. Miller, S.C. Wofsy, A.M. Michalak, E.A. Kort, A.E. Andrews, S.C. Biraud, E.J. Dlugokencky, J. Eluszkiewicz, M.L. Fischer, G. Janssens-Maenhout, B.R. Miller, J.B. Miller, S.A. Montzka, T. Nehrkorn, and C. Sweeney, "Anthropogenic emissions of methane in the United States", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 110, pp. 20018-20022, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1314392110
The new IPCC climate report
The time has come: the new IPCC report is here! After several years of work by over 800 scientists from around the world, and after days of extensive discussion at the IPCC plenary meeting in Stockholm, the Summary for Policymakers was formally adopted at 5 o’clock this morning. Congratulations to all the colleagues who were there and worked night shifts. The full text of the report will be available online beginning of next week. Realclimate summarizes the key findings and shows the most interesting graphs.
Update 29 Sept: Full (un-copyedited) report available here.
Global warming
It is now considered even more certain (> 95%) that human influence has been the dominant cause of the observed warming since the mid-20th century. Natural internal variability and natural external forcings (eg the sun) have contributed virtually nothing to the warming since 1950 – the share of these factors was narrowed down by IPCC to ± 0.1 degrees. The measured temperature evolution is shown in the following graph.
Figure 1 The measured global temperature curve from several data sets. Top: annual values. Bottom: averaged values over a decade.
[Read more…] about The new IPCC climate report
Arctic misrepresentations
At the weekend, Christopher Booker at the Daily Telegraph made another attempt (see previous) to downplay the obvious decreases in Arctic sea ice by (mis-)quoting a statement from Arctic oceanographer Ken Drinkwater and colleagues:
[Read more…] about Arctic misrepresentations
Ice hockey
Eric Steig
It is well known that ice shelves on the Antarctic Peninsula have collapsed on several occasions in the last couple of decades, that ice shelves in West Antarctica are thinning rapidly, and that the large outlet glaciers that drain the West Antarctic ice sheet (WAIS) are accelerating. The rapid drainage of the WAIS into the ocean is a major contributor to sea level rise (around 10% of the total, at the moment).
All of these observations match the response, predicted in the late 1970s by glaciologist John Mercer, of the Antarctic to anthropogenic global warming. As such, they are frequently taken as harbingers of greater future sea level rise to come. Are they?
Two papers published this week in Nature Geoscience provide new information that helps to address this question. One of the studies (led by me) says “probably”, while another (Abram et al.) gives a more definitive “yes”. [Read more…] about Ice hockey
2012 Updates to model-observation comparisons
Time for the 2012 updates!
As has become a habit (2009, 2010, 2011), here is a brief overview and update of some of the most discussed model/observation comparisons, updated to include 2012. I include comparisons of surface temperatures, sea ice and ocean heat content to the CMIP3 and Hansen et al (1988) simulations.
[Read more…] about 2012 Updates to model-observation comparisons
