Good thing? Of course.*
Nenana Ice Classic 2018
Another year, another ice out date. As in previous years, here’s an update of the Nenana Ice Classic time series (raw date, and then with a small adjustment for the calendrical variations in ‘spring’). One time series doesn’t prove much, but this is of course part of a much larger archive of phenomenological climate-related data that I’ve talked about before.
This year the ice on the Tanana River went out on May 1st, oddly enough the same date as last year, after another very warm (but quite snowy) Alaskan winter.
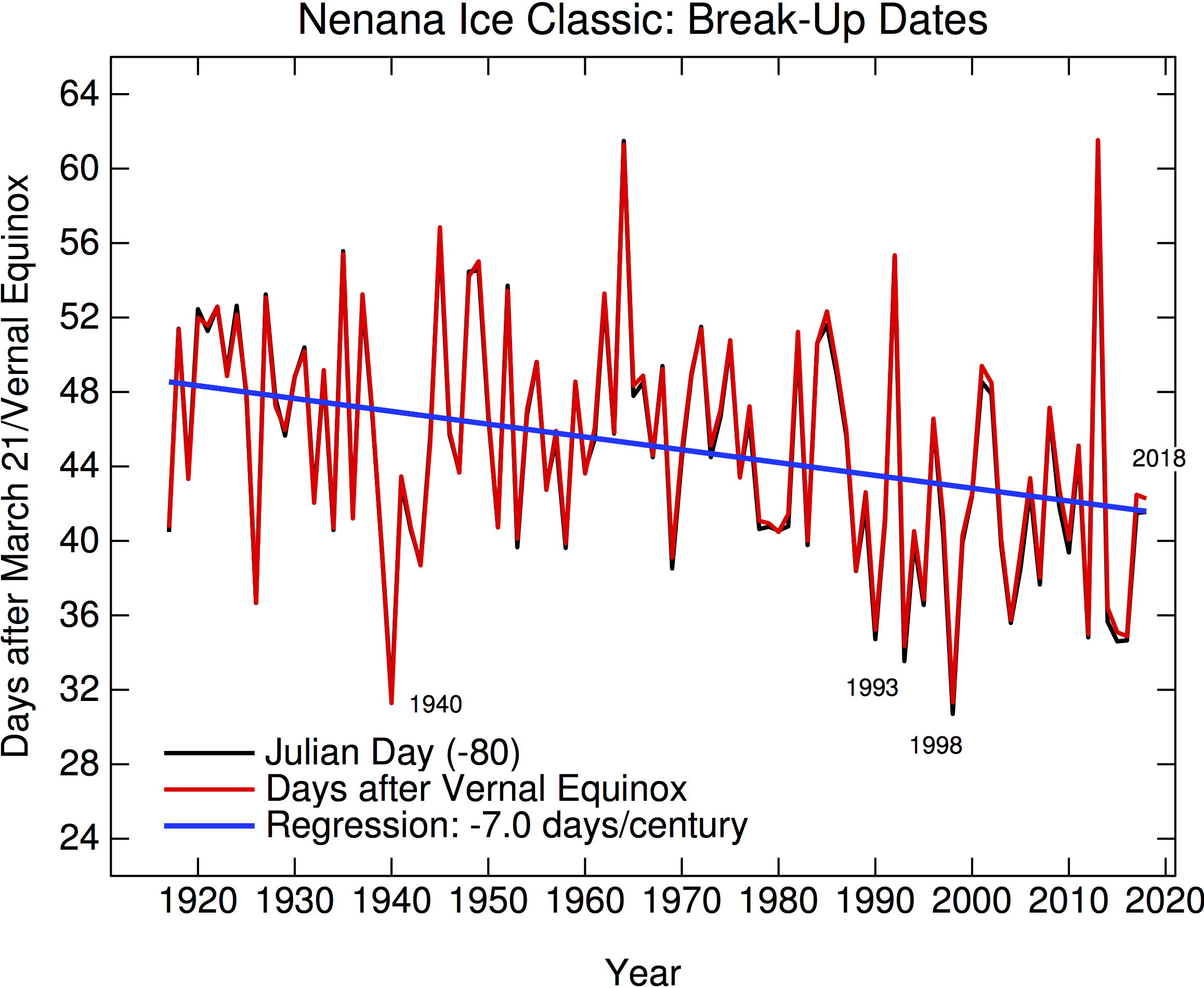
My shadow bet on whether any climate contrarian site will mention this dataset remains in play (none have since 2013 which was an record late year). [Update: It was mentioned on WUWT!]
The Silurian Hypothesis
One of the benefits of working for NASA is that the enormous range of science the agency covers – from satellite records for the present day, to exoplanet climates, from early Mars and deep time on Earth to the far future – and the opportunity to think ‘big’. This week sees the publication of a paper I wrote with Adam Frank that we hope might provoke some ‘big’ thinking.
The Silurian Hypothesis (preprint) is the idea if industrial civilization had arisen on Earth prior to the existence of hominids, what traces would be left that could be detectable now? As a starting point, we explore what the traces of the Anthropocene will be in millions of years – carbon isotope changes, global warming, increased sedimentation, spikes in heavy metal concentrations, plastics and more – and then look at previous examples of similar events in the geological record. What is unique about our presence on Earth and what might be common to any industrial civilization? Can we rule out similar causes?
[Read more…] about The Silurian Hypothesis
References
- G.A. Schmidt, and A. Frank, "The Silurian hypothesis: would it be possible to detect an industrial civilization in the geological record?", International Journal of Astrobiology, vol. 18, pp. 142-150, 2018. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S1473550418000095
Harde Times
Readers may recall a post a year ago about a nonsense paper by Hermann Harde that appeared in Global and Planetary Change. We reported too on the crowd-sourced rebuttal led by Peter Köhler that was published last October. Now comes an editorial by three members of the Editorial Board (Martin Grosjean, Joel Guiot and Zicheng Yu) reporting on what the circumstances were that led to the Harde paper appearing.
[Read more…] about Harde Times
References
- H. Harde, "Scrutinizing the carbon cycle and CO2 residence time in the atmosphere", Global and Planetary Change, vol. 152, pp. 19-26, 2017. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.02.009
- P. Köhler, J. Hauck, C. Völker, D.A. Wolf-Gladrow, M. Butzin, J.B. Halpern, K. Rice, and R.E. Zeebe, "Comment on “ Scrutinizing the carbon cycle and CO 2 residence time in the atmosphere ” by H. Harde", Global and Planetary Change, vol. 164, pp. 67-71, 2018. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.09.015
- M. Grosjean, J. Guiot, and Z. Yu, "Commentary", Global and Planetary Change, vol. 164, pp. 65-66, 2018. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.12.023
Alsup asks for answers
Some of you might have read about the lawsuit by a number of municipalities (including San Francisco and Oakland) against the major oil companies for damages (related primarily to sea level rise) caused by anthropogenic climate change. The legal details on standing, jurisdiction, etc. are all very interesting (follow @ColumbiaClimate for those details), but somewhat uniquely, the judge (William Alsup) has asked for a tutorial on climate science (2 hours of evidence from the plaintiffs and the defendents). Furthermore, he has posted a list of eight questions that he’d like the teams to answer.
More ice-out and skating day data sets
The responses to the last post on the Rideau Canal Skateway season changes were interesting, and led to a few pointers to additional data sets that show similar trends and some rather odd counter-points from the usual suspects.
[Read more…] about More ice-out and skating day data sets
Rideau Canal Skateway
I’ve been interested in indirect climate-related datasets for a while (for instance, the Nenana Ice Classic). One that I was reminded of yesterday is the 48-year series of openings and closings of the Rideau Canal Skateway in Ottawa.
IPCC Communication handbook
A new handbook on science communication came out from IPCC this week. Nominally it’s for climate science related communications, but it has a wider application as well. This arose mainly out of an “Expert meeting on Communication” that IPCC held in 2016.
6 principles to help IPCC scientists better communicate their work
There was a Guardian article on it as well.
The six principles are pretty straightforward:
- Be a confident communicator
- Talk about the real world, not abstract ideas
- Connect with what matters to your audience
- Tell a human story
- Lead with what you know
- Use the most effective visual communication
Each is supported with references to the relevant literature and with climate-related (“real world”) examples that are themselves confidently communicated with effective visuals.
But what do people think? Is this a useful addition to the literature on communication? Anything you think doesn’t work? or that perhaps surprises you?
PS. I’m perhaps a little biased because they use a Peter Essick photo for their cover art that was also in my book.
2017 temperature summary
This is a thread to discuss the surface temperature records that were all released yesterday (Jan 18). There is far too much data-vizualization on this to link to, but feel free to do so in the comments. Bottom line? It’s still getting warmer.
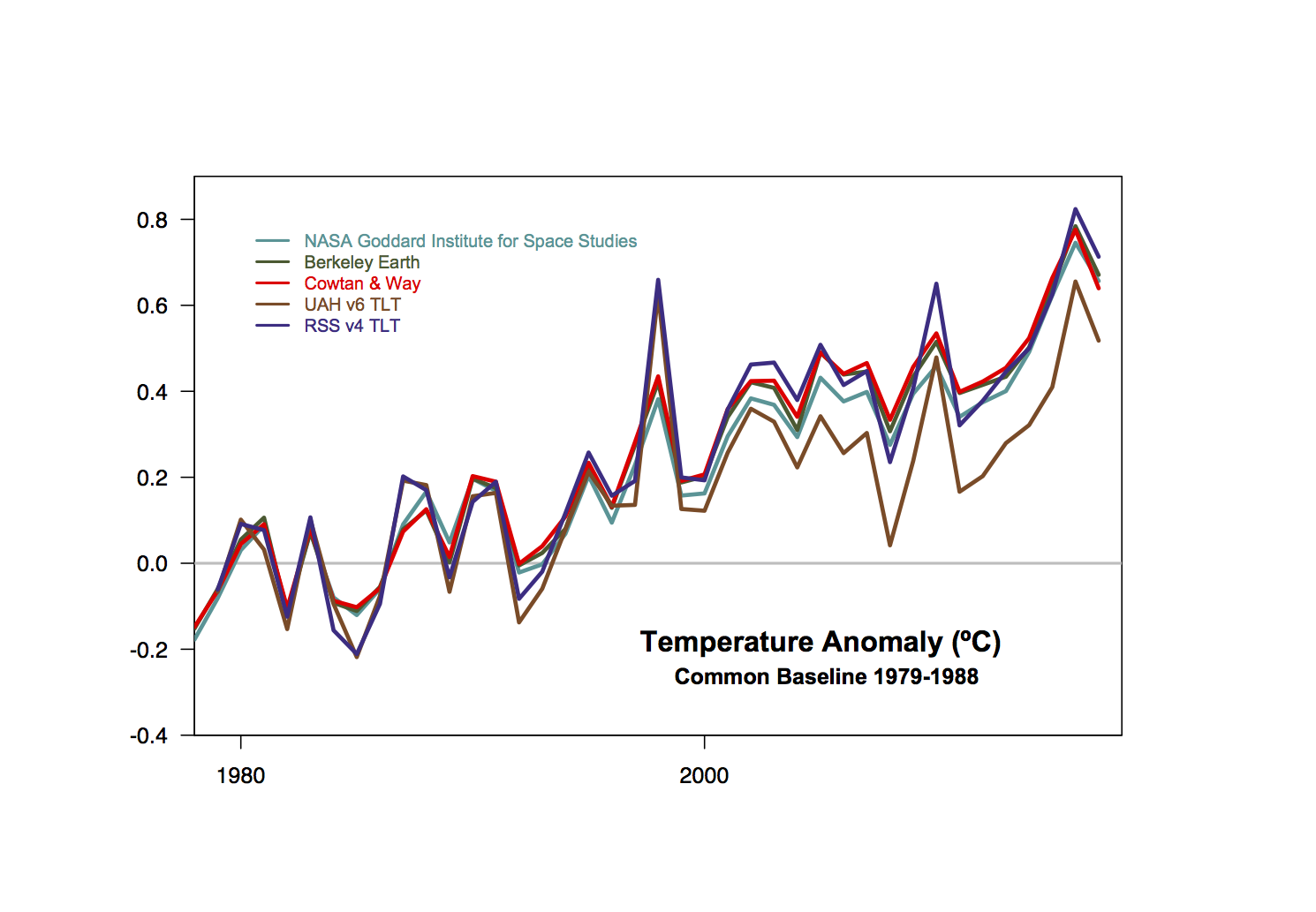
[Update: the page of model/observational data comparisons has now been updated too.]
What did NASA know? and when did they know it?
If you think you know why NASA did not report the discovery of the Antarctic polar ozone hole in 1984 before the publication of Farman et al in May 1985, you might well be wrong.
One of the most fun things in research is what happens when you try and find a reference to a commonly-known fact and slowly discover that your “fact” is not actually that factual, and that the real story is more interesting than you imagined…
[Read more…] about What did NASA know? and when did they know it?
References
- J.C. Farman, B.G. Gardiner, and J.D. Shanklin, "Large losses of total ozone in Antarctica reveal seasonal ClOx/NOx interaction", Nature, vol. 315, pp. 207-210, 1985. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/315207a0