This month’s open thread. Carbon budgets, Arctic sea ice minimum, methane emissions, hurricanes, volcanic impacts on climate… Please try and stick to these or similar topics.
Climate Science
Is there really still a chance for staying below 1.5 °C global warming?
There has been a bit of excitement and confusion this week about a new paper in Nature Geoscience, claiming that we can still limit global warming to below 1.5 °C above preindustrial temperatures, whilst emitting another ~800 Gigatons of carbon dioxide. That’s much more than previously thought, so how come? And while that sounds like very welcome good news, is it true? Here’s the key points.
Emissions budgets – a very useful concept
First of all – what the heck is an “emissions budget” for CO2? Behind this concept is the fact that the amount of global warming that is reached before temperatures stabilise depends (to good approximation) on the cumulative emissions of CO2, i.e. the grand total that humanity has emitted. That is because any additional amount of CO2 in the atmosphere will remain there for a very long time (to the extent that our emissions this century will like prevent the next Ice Age due to begin 50 000 years from now). That is quite different from many atmospheric pollutants that we are used to, for example smog. When you put filters on dirty power stations, the smog will disappear. When you do this ten years later, you just have to stand the smog for a further ten years before it goes away. Not so with CO2 and global warming. If you keep emitting CO2 for another ten years, CO2 levels in the atmosphere will increase further for another ten years, and then stay higher for centuries to come. Limiting global warming to a given level (like 1.5 °C) will require more and more rapid (and thus costly) emissions reductions with every year of delay, and simply become unattainable at some point.
It’s like having a limited amount of cake. If we eat it all in the morning, we won’t have any left in the afternoon. The debate about the size of the emissions budget is like a debate about how much cake we have left, and how long we can keep eating cake before it’s gone. Thus, the concept of an emissions budget is very useful to get the message across that the amount of CO2 that we can still emit in total (not per year) is limited if we want to stabilise global temperature at a given level, so any delay in reducing emissions can be detrimental – especially if we cross tipping points in the climate system, e.g trigger the complete loss of the Greenland Ice Sheet. Understanding this fact is critical, even if the exact size of the budget is not known.
But of course the question arises: how large is this budget? There is not one simple answer to this, because it depends on the choice of warming limit, on what happens with climate drivers other than CO2 (other greenhouse gases, aerosols), and (given there’s uncertainties) on the probability with which you want to stay below the chosen warming limit. Hence, depending on assumptions made, different groups of scientists will estimate different budget sizes.
Computing the budget
The standard approach to computing the remaining carbon budget is:
(1) Take a bunch of climate and carbon cycle models, start them from preindustrial conditions and find out after what amount of cumulative CO2 emissions they reach 1.5 °C (or 2 °C, or whatever limit you want).
(2) Estimate from historic fossil fuel use and deforestation data how much humanity has already emitted.
The difference between those two numbers is our remaining budget. But there are some problems with this. The first is that you’re taking the difference between two large and uncertain numbers, which is not a very robust approach. Millar et al. fixed this problem by starting the budget calculation in 2015, to directly determine the remaining budget up to 1.5 °C. This is good – in fact I suggested doing just that to my colleague Malte Meinshausen back in March. Two further problems will become apparent below, when we discuss the results of Millar et al.
So what did Millar and colleagues do?
A lot of people were asking this, since actually it was difficult to see right away why they got such a surprisingly large emissions budget for 1.5 °C. And indeed there is not one simple catch-all explanation. Several assumptions combined made the budget so big.
The temperature in 2015
To compute a budget from 2015 to “1.5 °C above preindustrial”, you first need to know at what temperature level above preindustrial 2015 was. And you have to remove short-term variability, because the Paris target applies to mean climate. Millar et al. concluded that 2015 was 0.93 °C above preindustrial. That’s a first point of criticism, because this estimate (as Millar confirmed to me by email) is entirely based on the Hadley Center temperature data, which notoriously have a huge data gap in the Arctic. (Here at RealClimate we were actually the first to discuss this problem, back in 2008.) As the Arctic has warmed far more than the global mean, this leads to an underestimate of global warming up to 2015, by 0.06 °C when compared to the Cowtan&Way data or by 0.17 °C when compared to the Berkeley Earth data, as Zeke Hausfather shows in detail over at Carbon Brief.
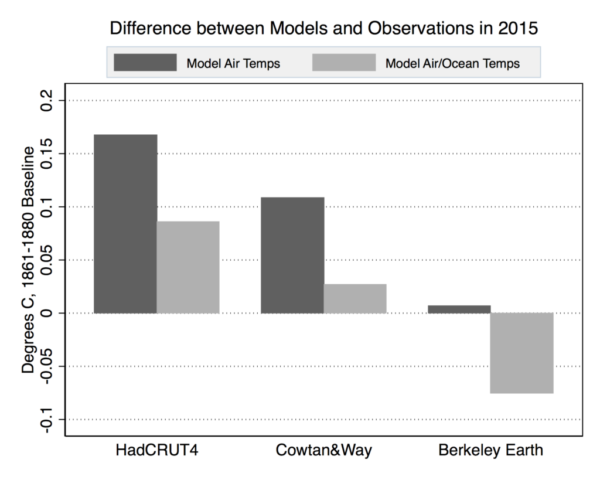
Figure: Difference between modeled and observed warming in 2015, with respect to the 1861-1880 average. Observational data has had short-term variability removed per the Otto et al 2015 approach used in the Millar et al 2017. Both RCP4.5 CMIP5 multimodel mean surface air temperatures (via KNMI) and blended surface air/ocean temperatures (via Cowtan et al 2015) are shown – the latter provide the proper “apples-to-apples” comparison. Chart by Carbon Brief.
As a matter of fact, as Hausfather shows in a second graph, HadCRUT4 is the outlier data set here, and given the Arctic data gap we’re pretty sure it is not the best data set. So, while the large budget of Millar et al. is based on the idea that we have 0.6 °C to go until 1.5 °C, if you believe (with good reason) that the Berkeley data are more accurate we only have 0.4 °C to go. That immediately cuts the budget of Millar et al. from 242 GtC to 152 GtC (their Table 2). [A note on units: you need to always check whether budgets are given in billion tons of carbon (GtC) or billion tons of carbon dioxide. 1 GtC = 3.7 GtCO2, so those 242 GtC are the same as 887 GtCO2.] Gavin managed to make this point in a tweet:
Headline claim from carbon budget paper that warming is 0.9ºC from pre-I is unsupported. Using globally complete estimates ~1.2ºC (in 2015) pic.twitter.com/B4iImGzeDE
— Gavin Schmidt (@ClimateOfGavin) September 20, 2017
Add to that the question of what years define the “preindustrial” baseline. Millar et al. use the period 1861-80. For example, Mike has argued that the period AD 1400-1800 would be a more appropriate preindustrial baseline (Schurer et al. 2017). That would add 0.2 °C to the anthropogenic warming that has already occurred, leaving us with just 0.2 °C and almost no budget to go until 1.5 °C. So in summary, the assumption by Millar et al. that we still have 0.6 °C to go up to 1.5 °C is at the extreme high end of how you might estimate that remaining temperature leeway, and that is one key reason why their budget is large. The second main reason follows.
To exceed or to avoid…
Here is another problem with the budget calculation: the model scenarios used for this actually exceed 1.5 °C warming. And the 1.5 °C budget is taken as the amount emitted by the time when the 1.5 °C line is crossed. Now if you stop emitting immediately at this point, of course global temperature will rise further. From sheer thermal inertia of the oceans, but also because if you close down all coal power stations etc., aerosol pollution in the atmosphere, which has a sizeable cooling effect, will go way down, while CO2 stays high. So with this kind of scenario you will not limit global warming to 1.5 °C. This is called a “threshold exceedance budget” or TEB – Glen Peters has a nice explainer on that (see his Fig. 3). All the headline budget numbers of Millar et al., shown in their Tables 1 and 2, are TEBs. What we need to know, though, is “threshold avoidance budgets”, or TAB, if we want to stay below 1.5 °C.
Millar et al also used a second method to compute budgets, shown in their Figure 3. However, as Millar told me in an email, these “simple model budgets are neither TEBs nor TABs (the 66 percentile line clearly exceeds 1.5 °C in Figure 3a), they are instead net budgets between the start of 2015 and the end of 2099.” What they are is budgets that cause temperature to exceed 1.5 °C in mid-century, but then global temperature goes back down to 1.5 °C in the year 2100!
In summary, both approaches used by Millar compute budgets that do not actually keep global warming to 1.5 °C.
How some media (usual suspects in fact) misreported
We’ve seen a bizarre (well, if you know the climate denialist scene, not so bizarre) misreporting about Millar et al., focusing on the claim that climate models have supposedly overestimated global warming. Carbon Brief and Climate Feedback both have good pieces up debunking this claim, so I won’t delve into it much. Let me just mention one key aspect that has been misunderstood. Millar et al. wrote the confusing sentence: “in the mean CMIP5 response cumulative emissions do not reach 545GtC until after 2020, by which time the CMIP5 ensemble-mean human-induced warming is over 0.3 °C warmer than the central estimate for human-induced warming to 2015”. As has been noted by others, this is comparing model temperatures after 2020 to an observation-based temperature in 2015, and of course the latter is lower – partly because it is based on HadCRUT4 data as discussed above, but equally so because of comparing different points in time. This is because it refers to the point when 545 GtC is reached. But the standard CMIP5 climate models used here are not actually driven by emissions at all, but by atmospheric CO2 concentrations. For the historic period, these are taken from observed data. So the fact that 545 GtC are reached too late doesn’t even refer to the usual climate model scenarios. It refers to estimates of emissions by carbon cycle models, which are run in an attempt to derive the emissions that would have led to the observed time evolution of CO2 concentration.
Does it all matter?
We still live in a world on a path to 3 or 4 °C global warming, waiting to finally turn the tide of rising emissions. At this point, debating whether we have 0.2 °C more or less to go until we reach 1.5 °C is an academic discussion at best, a distraction at worst. The big issue is that we need to see falling emissions globally very very soon if we even want to stay well below 2 °C. That was agreed as the weaker goal in Paris in a consensus by 195 nations. It is high time that everyone backs this up with actions, not just words.
Technical p.s. A couple of less important technical points. The estimate of 0.93 °C above 1861-80 used by Millar et al. is an estimate of the human-caused warming. I don’t know whether the Paris agreement specifies to limit human-caused warming, or just warming, to 1.5 °C – but in practice it does not matter, since the human-caused warming component is almost exactly 100 % of the observed warming. Using the same procedure as Millar yields 0.94 °C for total observed climate warming by 2015, according to Hausfather.
However, updating the statistical model used to derive the 0.93 °C anthropogenic warming to include data up to 2016 gives an anthropogenic warming of 0.96 °C in 2015.
Weblink
Statement by Millar and coauthors pushing back against media misreporting. Quote: “We find that, to likely meet the Paris goal, emission reductions would need to begin immediately and reach zero in less than 40 years’ time.”
Impressions from the European Meteorological Society’s annual meeting in Dublin
The 2017 annual assembly of the European Meteorological Society (EMS) had a new set-up with a plenary keynote each morning. I though some of these keynotes were very interesting. There was a talk by Florence Rabier from the European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), who presented the story of ensemble forecasting. Keith Seitter, the executive director of the American Meteorological Society (AMS), talked about the engagement with the society on the Wednesday.

[Read more…] about Impressions from the European Meteorological Society’s annual meeting in Dublin
Why extremes are expected to change with a global warming
Joanna Walters links extreme weather events with climate change in a recent article in the Guardian, however, some reservations have been expressed about such links in past discussions.
For example, we discussed the connection between single storms and global warming in the post Hurricanes and Global Warming – Is there a connection?, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has issued a statement, and Mike has recently explained the connection in the Guardian.
[Read more…] about Why extremes are expected to change with a global warming
Unforced Variations: Sep 2017
This month’s open thread…. and let’s stay on climate topics this month. It’s not like there isn’t anything climate-y to talk about (sea ice minimums, extreme events, climate model tunings, past ‘hyperthermals’… etc.). Anything too far off-topic will get binned. Thanks!
Data rescue projects
It’s often been said that while we can only gather new data about the planet at the rate of one year per year, rescuing old data can add far more data more quickly. Data rescue is however extremely labor intensive. Nonetheless there are multiple data rescue projects and citizen science efforts ongoing, some of which we have highlighted here before. For those looking for an intro into the subject, this 2014 article is an great introduction.

Weather diary from the the Observatoire de Paris, written by Giovanni Cassini on 18th January 1789.
I was asked this week whether there was a list of these projects, and with a bit of help from Twitter, we came up with the following:
- Old Weather (@oldweather)
- Weather Detective (closing soon)
- Weather Rescue
- NOAA Climate Database Modernization Program
- New Zealand (@DeepSouth_NZ)
- The International Environmental Data Rescue Organization (IEDRO)
- Atmospheric Circulation Reconstruction over the Earth (@met_acre)
- The International Data Rescue Portal (i-Dare)
- Met Éirann (poster)
- Historical Climatology (list of more databases)
- Data Rescue at home
- Historical Canadian data
- SE Australia Recent Climate History (no longer active?)
- Congo basin eco-climatological data recovery and valorisation (COBECORE)
- The climate and environmental history collaborative research environment (Tambora)
(If you know of any more, please add them in the comments, and I’ll try and keep this list up to date).
Sensible Questions on Climate Sensitivity
Guest Commentary by Cristian Proistosescu, Peter Huybers and Kyle Armour
tl;dr
Two recent papers help bridge a seeming gap between estimates of climate sensitivity from models and from observations of the global energy budget. Recognizing that equilibrium climate sensitivity cannot be directly observed because Earth’s energy balance is a long way from equilibrium, the studies instead focus on what can be inferred about climate sensitivity from historical trends. Calculating a climate sensitivity from the simulations that is directly comparable with that observed shows both are consistent. Crucial questions remain, however, regarding how climate sensitivity will evolve in the future.
[Read more…] about Sensible Questions on Climate Sensitivity
Observations, Reanalyses and the Elusive Absolute Global Mean Temperature
One of the most common questions that arises from analyses of the global surface temperature data sets is why they are almost always plotted as anomalies and not as absolute temperatures.
There are two very basic answers: First, looking at changes in data gets rid of biases at individual stations that don’t change in time (such as station location), and second, for surface temperatures at least, the correlation scale for anomalies is much larger (100’s km) than for absolute temperatures. The combination of these factors means it’s much easier to interpolate anomalies and estimate the global mean, than it would be if you were averaging absolute temperatures. This was explained many years ago (and again here).
Of course, the absolute temperature does matter in many situations (the freezing point of ice, emitted radiation, convection, health and ecosystem impacts, etc.) and so it’s worth calculating as well – even at the global scale. However, and this is important, because of the biases and the difficulty in interpolating, the estimates of the global mean absolute temperature are not as accurate as the year to year changes.
This means we need to very careful in combining these two analyses – and unfortunately, historically, we haven’t been and that is a continuing problem.
[Read more…] about Observations, Reanalyses and the Elusive Absolute Global Mean Temperature
Unforced Variations: August 2017
Joy plots for climate change
 This is joy as in ‘Joy Division’, not as in actual fun.
This is joy as in ‘Joy Division’, not as in actual fun.
Many of you will be familiar with the iconic cover of Joy Division’s Unknown Pleasures album, but maybe fewer will know that it’s a plot of signals from a pulsar (check out this Scientific American article on the history). The length of the line is matched to the frequency of the pulsing so that successive pulses are plotted almost on top of each other. For many years this kind of plot did not have a well-known designation until, in fact, April this year:
I hereby propose that we call these "joy plots" #rstats https://t.co/uuLGpQLAwY
— Jenny Bryan (@JennyBryan) April 25, 2017
So “joy plots” it is.