By Stefan Rahmstorf and Martin Vermeer
The scientific sea level discussion has moved a long way since the last IPCC report was published in 2007 (see our post back then). The Copenhagen Synthesis Report recently concluded that “The updated estimates of the future global mean sea level rise are about double the IPCC projections from 2007″. New Scientist last month ran a nice article on the state of the science, very much in the same vein. But now Mark Siddall, Thomas Stocker and Peter Clark have countered this trend in an article in Nature Geoscience, projecting a global rise of only 7 to 82 cm from 2000 to the end of this century.

Coastal erosion: Like the Dominican Republic, many island nations are
particularly vulnerable to sea level rise. (Photo: S.R.)

 One of my (Eric’s) favorite old books is The Starship and the Canoe by Kenneth Brower It’s a 1970s book about a father (Freeman Dyson, theoretical physicist living in Princeton) and son (George Dyson, hippy kayaker living 90 ft up in a fir tree in British Columbia) that couldn’t be more different, yet are strikingly similar in their originality and brilliance. I started out my career heading into astrophysics, and I’m also an avid sea kayaker and I grew up with the B.C. rainforest out my back door. So I think I have a sense of what drives these guys. Yet I’ve never understood how Freeman Dyson became such a climate contrarian and advocate for off-the-wall biogeoengineering solutions like carbon-eating trees, something we’ve
One of my (Eric’s) favorite old books is The Starship and the Canoe by Kenneth Brower It’s a 1970s book about a father (Freeman Dyson, theoretical physicist living in Princeton) and son (George Dyson, hippy kayaker living 90 ft up in a fir tree in British Columbia) that couldn’t be more different, yet are strikingly similar in their originality and brilliance. I started out my career heading into astrophysics, and I’m also an avid sea kayaker and I grew up with the B.C. rainforest out my back door. So I think I have a sense of what drives these guys. Yet I’ve never understood how Freeman Dyson became such a climate contrarian and advocate for off-the-wall biogeoengineering solutions like carbon-eating trees, something we’ve 
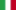
 New York Times,
New York Times,